
參照下列化學反應:
\[\text{2HI}\left( \text{g} \right)\ \to \ {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\ \text{+}\ {{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\]下表中,展示了不同溫度下該反應的速率常數:
| \(T\left( \text{K} \right)\) | \(k\left( \text{d}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\ {{\text{s}}^{-1}} \right)\) | \(T\left( \text{K} \right)\) | \(k\left( \text{d}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\ {{\text{s}}^{-1}} \right)\) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(598\) | \(2.29\times {{10}^{-6}}\) | \(648\) | \(4.27\times {{10}^{-5}}\) |
| \(698\) | \(4.79\times {{10}^{-4}}\) | \(748\) | \(3.89\times {{10}^{-3}}\) |
| \(798\) | \(2.88\times {{10}^{-2}}\) | \(848\) | \(1.51\times {{10}^{-1}}\) |
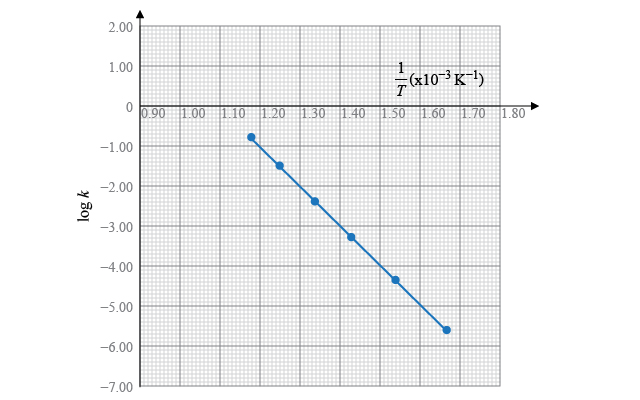
根據以上數據,在坐標紙上繪出 \(\log k\) 對 \(\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{T} }\) 的坐標圖,並回答下面的題目(已知氣體常數 \(R=8.31\ \text{J}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\);答案保留三位有效數字)。
| \(T\left( \text{K} \right)\) | \(\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{T}\left( \times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-\text{3}}}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}} \right) }\) | \(k\left( \text{d}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\ {{\text{s}}^{-1}} \right)\) | \(\log k\) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(598\) | \(1.67\) | \(2.29\times {{10}^{-6}}\) | \(-5.64\) |
| \(648\) | \(1.54\) | \(4.27\times {{10}^{-5}}\) | \(-4.37\) |
| \(698\) | \(1.43\) | \(4.79\times {{10}^{-4}}\) | \(-3.32\) |
| \(748\) | \(1.34\) | \(3.89\times {{10}^{-3}}\) | \(-2.41\) |
| \(798\) | \(1.25\) | \(2.88\times {{10}^{-2}}\) | \(-1.54\) |
| \(848\) | \(1.18\) | \(1.51\times {{10}^{-1}}\) | \(-0.82\) |
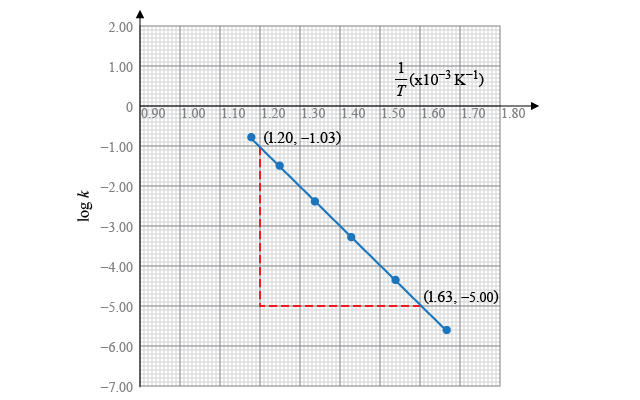
其中,\[\text{直線的斜率}=\frac{\left( -5.00 \right)-\left( -1.03 \right)}{\left( 1.63-1.20 \right)\times {{10}^{-3}}}=-9.23\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K}\]
所以,\[\text{直線的斜率}=-\frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{2.3R}=-9.23\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K}\]
即, \[\begin{align} & {{E}_{\text{A}}}=2.3\times 8.31\ \text{J}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\times 9.23\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K} \\ & \ \ \ \ \ \ =1.76 \times {{10}^{5}}\ \text{J}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}} \\ & \ \ \ \ \ \ =176\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}} \\ \end{align}\]
所以,反應的活化能為 \(176\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\)。
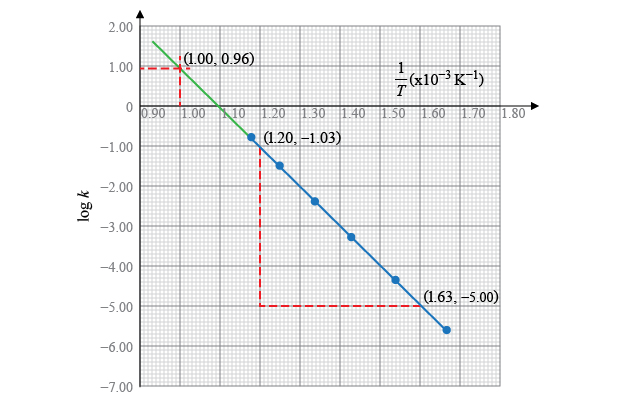
在 \(1 \ 000 \ \text{K}\) 時, \[\frac{1}{T}=\frac{1}{1\ 000\ \text{K}}\ =\ 1.00\times {{10}^{-3}}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\]
根據坐標圖可知,此時 \[\log k=0.96\]
即, \[k={{10}^{0.96}}=9.12\ \text{d}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\ {{\text{s}}^{-1}}\]
所以,\(1 \ 000 \ \text{K}\) 時,反應的速率常數為 \(9.12\ \text{d}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\ {{\text{s}}^{-1}}\)。
參照下列化學反應,
\[5\text{B}{{\text{r}}^{-}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\ +\ \text{Br}{{\text{O}}_{3}}^{-}\left( \text{aq} \right)\ +\ 6{{\text{H}}^{+}}\left( \text{aq} \right) \to \ 3\text{B}{{\text{r}}_{2}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\ +\ 3{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\left( \text{l} \right)\]一名同學嘗試利用微量化學反應來測定反應的活化能。實驗中,他在不同的溫度下,將相同成分的反應混合物混合,並使其發生反應。量度每個反應混合物生成相等微量的溴所需的時間,並列成下表。
| 溫度 \(T\left( ^{\text{o}}\text{C} \right)\) | \(25\) | \(35\) | \(45\) | \(55\) | \(65\) | \(75\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 時間 \(t\left( s \right)\) | \(74\) | \(37\) | \(19\) | \(11\) | \(6\) | \(?\) |
根據以上實驗數據,在坐標紙上繪製 \(\displaystyle{ \ln {\frac{1}{t}} }\) 對 \(\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{T} }\) 的坐標圖,並回答下列問題(已知氣體常數 \(R=8.31\ \text{J}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\);答案保留三位有效數字)。
實驗的原理:生成棕黃色的溴,會使反應混合物的顏色發生變化。實驗中,可以利用比色計測量溶液的吸光度。當反應混合物達至相同的吸光度時,即表示生成的溴的量相同,也就是測量的反應所需的時間 \(t\)。而反應速率,則與時間 \(t\) 成反比。即:
\[\text{反應速率}\ \text{∝}\ \frac{1}{t}\]所以,可用下式表示速率常數與時間 \(t\) 的關係:
\[k\ =\ \frac{c}{t}\]其中,\(c\) 是常數。
由阿列紐斯方程式:
\[\displaystyle{ k\ =\ A{{e}^{-\frac{{{E}_{A}}}{RT}}} }\]可知:
\[\displaystyle{ \ln k=\ln A-\frac{{{E}_{A}}}{RT}=\ln \frac{c}{t} }\]所以,
\[\displaystyle{ \ln \frac{1}{t}=-\frac{{{E}_{A}}}{R}\times \frac{1}{T}+\left( \ln A-\ln c \right) }\]若以 \(\displaystyle{ \ln {\frac{1}{t}} }\) 對 \(\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{T} }\) 繪製坐標圖,則直線的斜率就是 \(\displaystyle{ -\frac{{{E}_{A}}}{R} }\)。
| \(t\left( s \right)\) | \(\displaystyle{ \ln \frac{1}{t} }\) | \(T\left( \text{K} \right)\) | \(\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{T}\left( \times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}} \right) }\) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(74\) | \(-4.30\) | \(298\) | \(3.36\) |
| \(37\) | \(-3.61\) | \(308\) | \(3.25\) |
| \(19\) | \(-2.94\) | \(318\) | \(3.14\) |
| \(11\) | \(-2.40\) | \(328\) | \(3.05\) |
| \(6\) | \(-1.79\) | \(338\) | \(2.96\) |
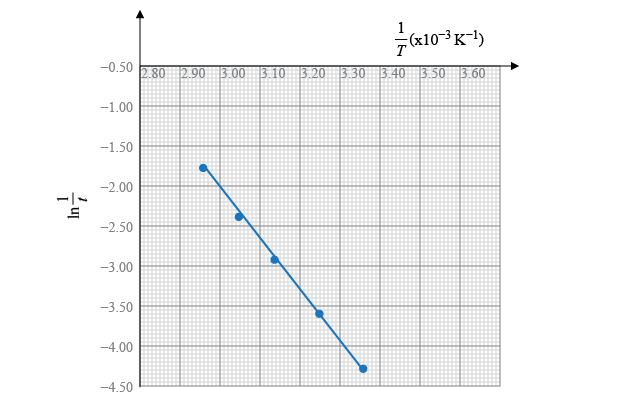
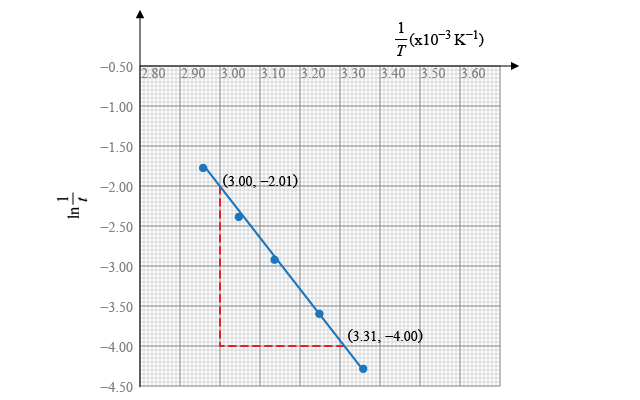
其中,
\[\text{直線的斜率}=\frac{\left( -4.00 \right)-\left( -2.01 \right)}{\left( 3.31-3.00 \right)\times {{10}^{-3}}}=-6.42\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K}\]所以,
\[\text{直線的斜率}=-\frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{R}=-6.42\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K}\]即,
\[\begin{align} & {{E}_{\text{A}}}=8.31\ \text{J}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\times 6.42\times {{10}^{3}}\ \text{K} \\ & \ \ \ \ \ \ =5.34 \times {{10}^{4}}\ \text{J}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}} \\ & \ \ \ \ \ \ =53.4\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}} \\ \end{align}\]所以,反應的活化能是 \(53.4\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\)。
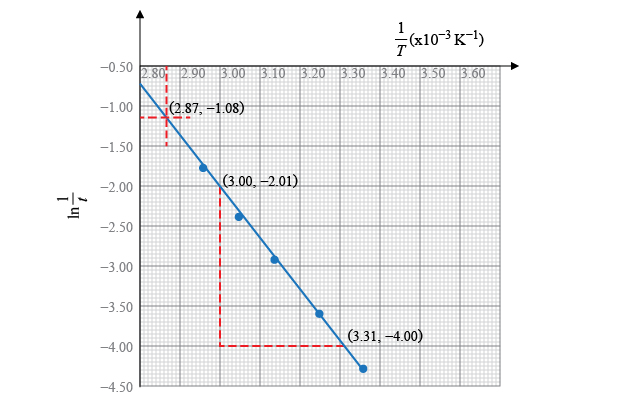
在 \(75{{\ }^{\text{o}}}\text{C}\) 時,
\[\frac{1}{T}=\frac{1}{\left( 75+273 \right)\ K}\ =\ 2.87\times {{10}^{-3}}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\]根據坐標圖可知,此時:
\[\ln \frac{1}{t}=-1.08\]即,
\[\frac{1}{t}={{e}^{-1.08}}=0.340\]所以,
\[t=2.94\ \text{s}\]所以,\(75{{\ }^{\text{o}}}\text{C}\) 時,反應所需的時間是 \(2.94\ \text{s}\)。
已知某一化學反應在 \(350\ \text{K}\) 下的速率常數是 \(338\ \text{K}\) 下速率常數的 \(9\) 倍。計算該反應的活化能(已知氣體常數 \(R\ =\ 8.31\ \text{J}\ {{\text{K}}^{-1}}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\);答案保留三位有效數字)。
題解:
根據阿列紐斯方程式的變化可知:
\(\displaystyle{ \ln \ {{k}_{1}}\ =\ \ln A\ -\ \frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{R{{T}_{\text{1}}}} }\)
\(\displaystyle{ \ln \ {{k}_{2}}\ =\ \ln A\ -\ \frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{R{{T}_{\text{2}}}} }\)
兩式相減就可以得到:
\[\ln \frac{{{k}_{2}}}{{{k}_{1}}}=\frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{R}\left( \frac{1}{{{T}_{1}}}-\frac{1}{{{T}_{2}}} \right)\]將題目中的數字帶入上式可得:
\[\ln \frac{9k}{k}=\frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{8.31}\left( \frac{1}{338}-\frac{1}{350} \right)\]即:
\[{{E}_{\text{A}}}=180\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\]所以,反應的活化能是 \(180\ \text{kJ}\ \text{mo}{{\text{l}}^{-1}}\)
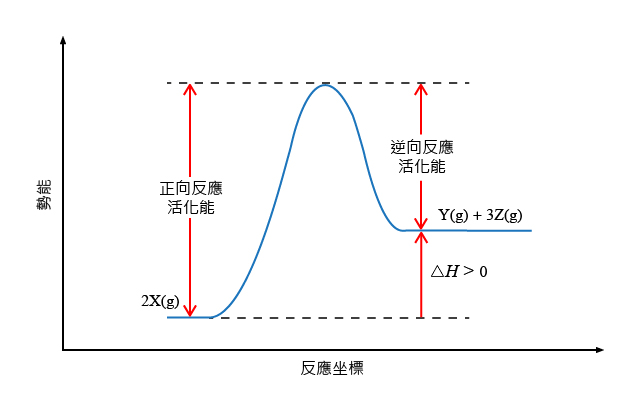
參照下列可逆反應:
\[\text{2X}\left( \text{g} \right)\ \rightleftharpoons \ \text{Y}\left( \text{g} \right)\ \text{+}\ \text{3Z}\left( \text{g} \right)\ \ \ \ \ \Delta H\ >\ 0\]升高溫度時,正向反應的速率常數和逆向反應的速率常數會發生甚麼變化?兩者的變化是否一致?
題解:
由於所涉及的可逆反應的正向反應是吸熱的(\(\Delta H\ >\ 0\)),所以正向反應的活化能大於逆向反應的活化能。反應的能線圖如下圖所示:
根據阿列紐斯方程式的對數變換:
\[\ln \frac{{{k}_{{{T}_{\text{2}}}}}}{{{k}_{{{T}_{\text{1}}}}}}=\frac{{{E}_{\text{A}}}}{R}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{{{T}_{\text{1}}}}-\frac{1}{{{T}_{\text{2}}}} \right)\]可知:
所以,升高溫度時,正向反應的速率常數和逆向反應的速率常數變大;而正向反應的速率升幅比逆向反應速率常數的升幅更大。